Epistemology
| Philosophy |
|---|

|
|
Branches
|
|
Eras
|
|
Traditions
|
|
Philosophers
Aestheticians · Epistemologists
Ethicists · Logicians Metaphysicians Social and political philosophers |
|
Literature
Aesthetics · Epistemology
Ethics · Logic · Metaphysics Political philosophy |
|
Lists
|
| Portal |
Epistemology (from Greek ἐπιστήμη – epistēmē, "knowledge, science" + λόγος, "logos") or theory of knowledge is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature and scope (limitations) of knowledge.[1] It addresses the questions:
- What is knowledge?
- How is knowledge acquired?
- What do people know?
- How do we know what we know?
Much of the debate in this field has focused on analyzing the nature of knowledge and how it relates to connected notions such as truth, belief, and justification. It also deals with the means of production of knowledge, as well as skepticism about different knowledge claims.
The term was introduced into English by the Scottish philosopher James Frederick Ferrier (1808–1864).[2]
Contents |
Knowledge
Knowledge that, knowledge how, and knowledge by acquaintance
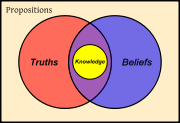
In this article, and in epistemology in general, the kind of knowledge usually discussed is propositional knowledge, also known as "knowledge that". How is such knowledge related to "knowledge how" and "acquaintance-knowledge"? For example: in mathematics, it is known that 2 + 2 = 4, but there is also knowing how to add two numbers and knowing a person (e.g., oneself), place (e.g., one's hometown), thing (e.g., cars), or activity (e.g., addition). Some (though not all) philosophers think there is an important distinction between "knowing that", "knowing how", and "acquaintance-knowledge", with epistemology primarily interested in the first.[3]
Bertrand Russell is famous for distinguishing "knowledge by description" (a form of knowledge that) and "knowledge by acquaintance" in Problems of Philosophy. Gilbert Ryle is often credited with emphasizing the distinction between knowing how and knowing that in The Concept of Mind. In Personal Knowledge, Michael Polanyi argues for the epistemological relevance of knowledge how and knowledge that; using the example of the act of balance involved in riding a bicycle, he suggests that the theoretical knowledge of the physics involved in maintaining a state of balance cannot substitute for the practical knowledge of how to ride, and that it is important to understand how both are established and grounded. This position is essentially Ryle's, who argued that a failure to acknowledge the distinction between knowledge that and knowledge how leads to vicious regresses.
In recent times, some epistemologists (Sosa, Greco, Kvanvig, Zagzebski) have argued that epistemology should evaluate people's properties (i.e., intellectual virtues) and not just the properties of propositions or propositional mental attitudes. One reason is that higher forms of cognitive success (i.e., understanding) are said to involve features that can't be evaluated from a justified true belief view of knowledge.
Belief
| Certainty series |
|---|
| Agnosticism Belief Certainty Doubt Determinism Epistemology Estimation Fallibilism Fatalism Justification Nihilism Probability Skepticism Solipsism Truth Uncertainty |
Statements of "belief" sometimes mean the speaker predicts something that would prove to be useful or successful in some sense—perhaps the speaker might "believe in" his or her favorite football team. This is not the kind of belief usually addressed within epistemology. The kind dealt with is when "to believe something" simply means any cognitive content held as true. For example, to believe that the sky is blue is to think that the proposition "The sky is blue" is true.
Knowledge entails belief, so the statement, "I know the sky is blue, but I don't believe it", is self-contradictory.
Belief is a subjective personal basis for individual behavior, while truth is an objective state independent of the individual i.e. a fact.
Truth
Whether someone's belief is true is not a prerequisite for its belief. On the other hand, if something is actually known, then it categorically cannot be false. For example, a person believes that a particular bridge is safe enough to support him, and attempts to cross it; unfortunately, the bridge collapses under his weight. It could be said that he believed that the bridge was safe, but that this belief was mistaken. It would not be accurate to say that he knew that the bridge was safe, because plainly it was not. By contrast, if the bridge actually supported his weight then he might be justified in subsequently holding that he knew the bridge had been safe enough for his passage, at least at that particular time. For something to count as knowledge, it must actually be true. There is a sense that makes us feel that the truth should command our belief.
The Aristotelian definition of truth states:
"To say of something which is that it is not, or to say of something which is not that it is, is false. However, to say of something which is that it is, or of something which is not that it is not, is true."
Justification
In Plato's dialogue Theaetetus, Socrates considers a number of theories as to what knowledge is, the last being that knowledge is true belief that has been "given an account of" — meaning explained or defined in some way. According to the theory that knowledge is justified true belief, in order to know that a given proposition is true, one must not only believe the relevant true proposition, but one must also have a good reason for doing so. One implication of this would be that no one would gain knowledge just by believing something that happened to be true. For example, an ill person with no medical training, but a generally optimistic attitude, might believe that they will recover from their illness quickly. Nevertheless, even if this belief turned out to be true, the patient would not have known that they would get well since their belief lacked justification. The definition of knowledge as justified true belief was widely accepted until the 1960s. At this time, a paper written by the American philosopher Edmund Gettier provoked major widespread discussion. See theories of justification for other views on the idea.
The Gettier problem
Edmund Gettier is remembered for his 1963 argument which called into question the theory of knowledge that had been dominant among philosophers for thousands of years.[4] In a few pages, Gettier argued that there are situations in which one's belief may be justified and true, yet fail to count as knowledge. That is, Gettier contended that while justified belief in a true proposition is necessary for that proposition to be known, it is not sufficient. As in the diagram above, a true proposition can be believed by an individual (purple region) but still not fall within the "knowledge" category (yellow region).
According to Gettier, there are certain circumstances in which one does not have knowledge, even when all of the above conditions are met. Gettier proposed two thought experiments, which have come to be known as "Gettier cases," as counterexamples to the classical account of knowledge. One of the cases involves two men, Smith and Jones, who are awaiting the results of their applications for the same job. Each man has ten coins in his pocket. Smith has excellent reasons to believe that Jones will get the job and, furthermore, knows that Jones has ten coins in his pocket (he recently counted them). From this Smith infers, "the man who will get the job has ten coins in his pocket." However, Smith is unaware that he also has ten coins in his own pocket. Furthermore, Smith, not Jones, is going to get the job. While Smith has strong evidence to believe that Jones will get the job, he is wrong. Smith has a justified true belief that a man with ten coins in his pocket will get the job; however, according to Gettier, Smith does not know that a man with ten coins in his pocket will get the job, because Smith's belief is "...true by virtue of the number of coins in Jones's pocket, while Smith does not know how many coins are in Smith's pocket, and bases his belief...on a count of the coins in Jones's pocket, whom he falsely believes to be the man who will get the job." (see [4] p. 122.) These cases fail to be knowledge because the subject's belief is justified, but only happens to be true by virtue of luck (in other words, he made the correct choice {in this case predicting an outcome} for the wrong reasons).
It is far from clear that Gettier was the first to present this challenge to the justified-true-belief triumvirate. Some scholars attribute an extremely similar idea to Bertrand Russell.
Responses to Gettier
The responses to Gettier have been varied. Usually, they have involved substantive attempts to provide a definition of knowledge different from the classical one, either by recasting knowledge as justified true belief with some additional fourth condition, or as something else altogether.
Infallibilism, indefeasibility
In one response to Gettier, the American philosopher Richard Kirkham has argued that the only definition of knowledge that could ever be immune to all counterexamples is the infallibilist one.[5] To qualify as an item of knowledge, goes the theory, a belief must not only be true and justified, the justification of the belief must necessitate its truth. In other words, the justification for the belief must be infallible. (See Fallibilism, below, for more information.)
Yet another possible candidate for the fourth condition of knowledge is indefeasibility. Defeasibility theory maintains that there should be no overriding or defeating truths for the reasons that justify one's belief. For example, suppose that person S believes he saw Tom Grabit steal a book from the library and uses this to justify the claim that Tom Grabit stole a book from the library. A possible defeater or overriding proposition for such a claim could be a true proposition like, "Tom Grabit's identical twin Sam is currently in the same town as Tom." When no defeaters of one's justification exist, a subject would be epistemically justified.
The Indian philosopher B K Matilal has drawn on the Navya-Nyaya fallibilism tradition to respond to the Gettier problem. Nyaya theory distinguishes between know p and know that one knows p – these are different events, with different causal conditions. The second level is a sort of implicit inference that usually follows immediately the episode of knowing p (knowledge simpliciter). The Gettier case is analyzed by referring to a view of Gangesha (13th c.), who takes any true belief to be knowledge; thus a true belief acquired through a wrong route may just be regarded as knowledge simpliciter on this view. The question of justification arises only at the second level, when one considers the knowledgehood of the acquired belief. Initially, there is lack of uncertainty, so it becomes a true belief. But at the very next moment, when the hearer is about to embark upon the venture of knowing whether he knows p, doubts may arise. "If, in some Gettier-like cases, I am wrong in my inference about the knowledgehood of the given occurrent belief (for the evidence may be pseudo-evidence), then I am mistaken about the truth of my belief – and this is in accord with Nyaya fallibilism: not all knowledge-claims can be sustained."[6]
Reliabilism
Reliabilism is a theory that suggests a belief is justified (or otherwise supported in such a way as to count towards knowledge) only if it is produced by processes that typically yield a sufficiently high ratio of true to false beliefs. In other words, this theory states that a true belief counts as knowledge only if it is produced by a reliable belief-forming process.
Reliabilism has been challenged by Gettier cases. Another argument that challenges reliabilism, like the Gettier cases (although it was not presented in the same short article as the Gettier cases), is the case of Henry and the barn façades. In the thought experiment, a man, Henry, is driving along and sees a number of buildings that resemble barns. Based on his perception of one of these, he concludes that he has just seen barns. While he has seen one, and the perception he based his belief on was of a real barn, all the other barn-like buildings he saw were façades. Theoretically, Henry doesn't know that he has seen a barn, despite both his belief that he has seen one being true and his belief being formed on the basis of a reliable process (i.e. his vision), since he only acquired his true belief by accident.[7]
Other responses
The American philosopher Robert Nozick has offered the following definition of knowledge:
S knows that P if and only if:
- P;
- S believes that P;
- if P were false, S would not believe that P;
- if P is true, S will believe that P.[8]
Nozick believed that the third subjunctive condition served to address cases of the sort described by Gettier. Nozick further claims this condition addresses a case of the sort described by D. M. Armstrong:[9] A father believes his son innocent of committing a particular crime, both because of faith in his son and (now) because he has seen presented in the courtroom a conclusive demonstration of his son's innocence. His belief via the method of the courtroom satisfies the four subjunctive conditions, but his faith-based belief does not. If his son were guilty, he would still believe him innocent, on the basis of faith in his son; this would violate the third subjunctive condition.
The British philosopher Simon Blackburn has criticized this formulation by suggesting that we do not want to accept as knowledge beliefs which, while they "track the truth" (as Nozick's account requires), are not held for appropriate reasons. He says that "we do not want to award the title of knowing something to someone who is only meeting the conditions through a defect, flaw, or failure, compared with someone else who is not meeting the conditions.". In addition to this, externalist accounts of knowledge, like Nozick's, are often forced to reject closure in cases where it is intuitively valid.
Timothy Williamson has advanced a theory of knowledge according to which knowledge is not justified true belief plus some extra condition(s). In his book Knowledge and its Limits, Williamson argues that the concept of knowledge cannot be analyzed into a set of other concepts—instead, it is sui generis. Thus, though knowledge requires justification, truth, and belief, the word "knowledge" can't be, according to Williamson's theory, accurately regarded as simply shorthand for "justified true belief."
Externalism and internalism
Part of the debate over the nature of knowledge is a debate between epistemological externalists on the one hand, and epistemological internalists on the other. Externalists think that factors deemed "external", meaning outside of the psychological states of those who gain knowledge, can be conditions of knowledge. For example, an externalist response to the Gettier problem is to say that, in order for a justified true belief to count as knowledge, it must be caused, in the right sort of way, by relevant facts. Such causation, to the extent that it is "outside" the mind, would count as an external, knowledge-yielding condition. Internalists, contrariwise, claim that all knowledge-yielding conditions are within the psychological states of those who gain knowledge.
René Descartes, prominent philosopher and supporter of internalism wrote that, since the only method by which we perceive the external world is through our senses, and that, since the senses are not infallible, we should not consider our concept of knowledge to be infallible. The only way to find anything that could be described as "infallibly true," he advocates, would be to pretend that an omnipotent, deceitful being is tampering with one's perception of the universe, and that the logical thing to do is to question anything that involves the senses. "Cogito ergo sum" (I think, therefore I am) is commonly associated with Descartes' theory, because he postulated that the only thing that he could not logically bring himself to doubt is his own existence: "I do not exist" is a contradiction in terms; the act of saying that one does not exist assumes that someone must be making the statement in the first place. Though Descartes could doubt his senses, his body and the world around him, he could not deny his own existence, because he was able to doubt and must exist in order to do so. Even if some "evil genius" were to be deceiving him, he would have to exist in order to be deceived. However from this Descartes did not go as far as to define what he was. This was pointed out by the materialist philosopher Pierre Gassendi (1592–1655) who accused Descartes of saying that he was "not this and not that," while never saying what exactly was existing. One could argue that this is not an edifying question, because it doesn't matter what exactly exists, it only matters that it does indeed exist.
Acquiring knowledge
The second question that will be dealt with is the question of how knowledge is acquired. This area of epistemology covers:
- Issues concerning epistemic distinctions such as that between experience and apriori as means of creating knowledge.
- Distinguish between synthesis and analysis used as means of proof
- Debates such as the one between empiricists and rationalists.
- What is called "the regress problem"
A priori and a posteriori knowledge
The nature of this distinction has been disputed by various philosophers; however, the terms may be roughly defined as follows:
- A priori knowledge is knowledge that is known independently of experience (that is, it is non-empirical, or arrived at beforehand).
- A posteriori knowledge is knowledge that is known by experience (that is, it is empirical, or arrived at afterward).
Analytic/synthetic distinction
Some propositions are such that we appear to be justified in believing them just so far as we understand their meaning. For example, consider, "My father's brother is my uncle." We seem to be justified in believing it to be true by virtue of our knowledge of what its terms mean. Philosophers call such propositions "analytic." Synthetic propositions, on the other hand, have distinct subjects and predicates. An example of a synthetic proposition would be, "My father's brother has black hair." Kant held that all mathematical propositions are synthetic.
The American philosopher W. V. O. Quine, in his "Two Dogmas of Empiricism", famously challenged the distinction, arguing that the two have a blurry boundary.
Specific theories of knowledge acquisition
Empiricism
In philosophy, empiricism is generally a theory of knowledge emphasizing the role of experience, especially experience based on perceptual observations by the five senses. Certain forms treat all knowledge as empirical, while some regard disciplines such as mathematics and logic as exceptions.
Rationalism
Rationalists believe that knowledge is primarily (at least in some areas) acquired by a priori processes or is innate—for example, in the form of concepts not derived from experience. The relevant theoretical processes often go by the name "intuition". The relevant theoretical concepts may purportedly be part of the structure of the human mind (as in Kant's theory of transcendental idealism), or they may be said to exist independently of the mind (as in Plato's theory of Forms).
The extent to which this innate human knowledge is emphasized over experience as a means to acquire knowledge varies from rationalist to rationalist. Some hold that knowledge of any kind can only be gained a priori, while others claim that some knowledge can also be gained a posteriori. Consequently, the borderline between rationalist epistemologies and others can be vague.
Constructivism
Constructivism is a view in philosophy according to which all knowledge is "constructed" in as much as it is contingent on convention, human perception, and social experience. Constructivism proposes new definitions for knowledge and truth that form a new paradigm, based on inter-subjectivity instead of the classical objectivity, and on viability instead of truth. Piagetian constructivism, however, believes in objectivity—constructs can be validated through experimentation. The constructivist point of view is pragmatic; as Vico said: "The norm of the truth is to have made it."
It originated in sociology under the term "social constructionism" and has been given the name "constructivism" when referring to philosophical epistemology, though "constructionism" and "constructivism" are often used interchangeably. Constructivism has also emerged in the field of International Relations, where the writings of Alexander Wendt are popular. Describing the characteristic nature of International reality marked by 'anarchy' he says, "Anarchy is what states make of it."
The regress problem
". . . to justify a belief one must appeal to a further justified belief. This means that one of two things can be the case. Either there are some [epistemologically basic] beliefs that we can be justified in holding without being able to justify them on the basis of any other belief, or else for each justified belief there is an infinite regress of (potential) justification [the nebula theory]. On this theory there is no rock bottom of justification. Justification just meanders in and out through our network of beliefs, stopping nowhere." [10] The apparent impossibility of completing an infinite chain of reasoning is thought by some to support skepticism. "The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing ." (Socrates)
Response to the regress problem
Many epistemologists studying justification have attempted to argue for various types of chains of reasoning that can escape the regress problem.
Infinitism
It is not impossible for an infinite justificatory series to exist. This position is known as "infinitism". Infinitists typically take the infinite series to be merely potential, in the sense that an individual may have indefinitely many reasons available to him, without having consciously thought through all of these reasons when the need arises. This position is motivated in part by the desire to avoid what is seen as the arbitrariness and circularity of its chief competitors, foundationalism and coherentism. In mathematics, an infinite series will often converge – (this is the basis of calculus) – one can therefore have an infinite series of logical arguments and analyze it for a convergent (or non-convergent) solution.
Foundationalism
Foundationalists respond to the regress problem by claiming that some beliefs that support other beliefs do not themselves require justification by other beliefs. Sometimes, these beliefs, labeled "foundational," are characterized as beliefs of whose truth one is directly aware, or as beliefs that are self-justifying, or as beliefs that are infallible. According to one particularly permissive form of foundationalism, a belief may count as foundational, in the sense that it may be presumed true until defeating evidence appears, as long as the belief seems to its believer to be true. Others have argued that a belief is justified if it is based on perception or certain a priori considerations.
The chief criticism of foundationalism is that it allegedly leads to the arbitrary or unjustified acceptance of certain beliefs.[11]
Coherentism
Another response to the regress problem is coherentism, which is the rejection of the assumption that the regress proceeds according to a pattern of linear justification. To avoid the charge of circularity, coherentists hold that an individual belief is justified circularly by the way it fits together (coheres) with the rest of the belief system of which it is a part. This theory has the advantage of avoiding the infinite regress without claiming special, possibly arbitrary status for some particular class of beliefs. Yet, since a system can be coherent while also being wrong, coherentists face the difficulty of ensuring that the whole system corresponds to reality.
Foundherentism
There is also a position known as "foundherentism". Susan Haack is the philosopher who conceived it, and it is meant to be a unification of foundationalism and coherentism. One component of this theory is what is called the "analogy of the crossword puzzle." Whereas, say, infinists regard the regress of reasons as "shaped" like a single line, Susan Haack has argued that it is more like a crossword puzzle, with multiple lines mutually supporting each other.[12]
What do people know?
The last question that will be dealt with is the question of what people know. At the heart of this area of study is skepticism, with many approaches involved trying to disprove some particular form of it.
Skepticism
Skepticism is related to the question of whether certain knowledge is possible. "If we cannot move on to point B until we have proved point A, and if in order to prove point A we must establish it with absolute certainty, then it looks as though we will have a very hard time proving any point at all." Skeptics argue that the belief in something does not necessarily justify an assertion of knowledge of it. In this skeptics oppose foundationalism, which states that there have to be some basic beliefs that are justified without reference to others. The skeptical response to this can take several approaches. First, claiming that "basic beliefs" must exist, amounts to the logical fallacy of argument from ignorance combined with the slippery slope. While a foundationalist would use Münchhausen Trilemma as a justification for demanding the validity of basic beliefs, a skeptic would see no problem with admitting the result.
Developments from skepticism
Early in the 20th century, the notion that belief had to be justified as such to count as knowledge lost favour. Fallibilism is the view that knowing something does not entail certainty regarding it. Charles Sanders Peirce was a fallibilist and the most developed form of fallibilism can be traced to Karl Popper (1902–1994) whose first book Logik Der Forschung (The Logic of Investigation), 1934 introduced a "conjectural turn" into the philosophy of science and epistemology at large. He adumbrated a school of thought that is known as Critical Rationalism with a central tenet being the rejection of the idea that knowledge can ever be justified in the strong form that is sought by most schools of thought. His two most helpful exponents are the late William W Bartley and David Miller, recently retired from the University of Warwick. A major source of on-line material is the Critical Rationalist website and also the Rathouse of Rafe Champion.
Practical applications
Far from being purely academic, the study of epistemology is useful for a great many applications. It is particularly commonly employed in issues of law where proof of guilt or innocence may be required, or when it must be determined whether a person knew a particular fact before taking a specific action (e.g., whether an action was premeditated). Another practical application is to the design of computer interfaces. For example, the skills, rules, and knowledge taxonomy of human behavior has been used by designers to develop systems that are compatible with multiple "ways of knowing": abstract analytic reasoning, experience-based 'gut feelings', and 'craft' sensorimotor skills.
Other common applications of epistemology include:
|
|
See also
- Adaptive representation
- Agnotology
- Analytic tradition
- Bayesian probability
- Buddhist epistemology
- Conveyed concept
- Cybernetic epistemology
- Constructivist epistemology
- Eastern epistemology
- Evidentialism
- Evidentiality
- Explanatory model
- Formal epistemology
- General Semantics
- Knowledge by acquaintance
- Knowledge by description
- List of epistemology topics
- Meta-epistemology
- Methodology
- Methods of obtaining knowledge
- Monopolies of knowledge
- Mysticism
- Noölogy
- Participatory epistemology
- Philosophical Studies
- Physical ontology
- Platonic epistemology
- Praxeology
- Reason
- Reformed epistemology
- Revelation
- Scientific method
- Self-evidence
- Social epistemology
- Sociology of knowledge
- Transcendence (philosophy)
- Virtue epistemology
Sources
Footnotes
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Volume 3, 1967, Macmillan, Inc.
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Britannica Online, 2007
- ↑ It is sometimes suggested that these distinctions are recognized linguistically in some languages, even if not in modern Standard English (N.B. some languages related to English have been said to retain these verbs, e.g. Scots: "wit" and "ken"). In French, Portuguese and Spanish, to know (a person) is translated using connaître, conhecer, and conocer, respectively, whereas to know (how to do something) is translated using savoir, saber, and saber. Modern Greek has the verbs γνωρίζω (gnorízo) and ξέρω (kséro). Italian has the verbs conoscere and sapere and the nouns for knowledge are conoscenza and sapienza. German has the verbs kennen and wissen. Wissen implies knowing a fact, kennen implies knowing in the sense of being acquainted with and having a working knowledge of; there is also a noun derived from kennen, namely erkennen, which has been said to imply knowledge in the form of recognition or acknowledgment. The verb itself implies a process: you have to go from one state to another, from a state of "not-erkennen" to a state of true erkennen. This verb seems to be the most appropriate in terms of describing the "episteme" in one of the modern European languages, hence the German name "Erkenntnistheorie". The theoretical interpretation and significance of these linguistic issues remain controversial.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Gettier, Edmund (1963). "Is Justified True Belief Knowledge?". Analysis 23 (6): 121–23. doi:10.2307/3326922. http://jstor.org/stable/3326922.
- ↑ http://www.centenary.edu/attachments/philosophy/aizawa/courses/epistemologyf2008/kirkham1984.pdf
- ↑ Bimal Krishna Matilal (1986). Perception: An essay on Classical Indian Theories of Knowledge. Oxford India 2002. ISBN 0198246250.The Gettier problem is dealt with in Chapter 4, Knowledge as a mental episode. The thread continues in the next chapter Knowing that one knows. It is also discussed in Matilal's Word and the World p. 71-72.
- ↑ Goldman, Alan H. (December 1976). "Appearing as Irreducible in Perception". Philosophy and Phenomenological Research (International Phenomenological Society) 37 (2): 147–164. doi:10.2307/2107188. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2107188.
- ↑ Robert Nozick (1981). Philosophical Explanations. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674664485.Philosophical Explanations Chapter 3 "Knowledge and Skepticism" I. Knowledge Conditions for Knowledge p. 172-178.
- ↑ D. M. Armstrong (1973). Belief, Truth and Knowledge. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521097371.
- ↑ John L. Pollock (1975). Knowledge and Justification. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey. ISBN 0691072035. p. 26.
- ↑ Foundational Theories of Epistemic Justification entry in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- ↑ Susan Haack (1993). Evidence and Inquiry: Towards Reconstruction in Epistemology. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 063119679X.
Bibliography
- The London Philosophy Study Guide offers many suggestions on what to read, depending on the student's familiarity with the subject: Epistemology & Methodology
- Annis, David. 1978. "A Contextualist Theory of Epistemic Justification", in American Philosophical Quarterly, 15: 213–219.
- Ayer, Alfred Jules. 1936. Language, Truth, and Logic.
- BonJour, Laurence. 2002. Epistemology: Classic Problems and Contemporary Responses. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
- Boufoy-Bastick, Z. 2005. "Introducing 'Applicable Knowledge' as a Challenge to the Attainment of Absolute Knowledge", Sophia Journal of Philosophy, 8: 39–51.
- Bovens, Luc & Hartmann, Stephan. 2003. Bayesian Epistemology. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Butchvarov, Panayot. 1970. The Concept of Knowledge. Evanston, Northwestern University Press.
- Cohen, Stewart. 1998. "Contextualist Solutions to Epistemological Problems: Skepticism, Gettier, and the Lottery." Australasian Journal of Philosophy, 76: 289–306.
- Cohen, Stewart. 1999. "Contextualism, Skepticism, and Reasons", in Tomberlin 1999.
- Dancy, Jonathan. 1991. An Introduction to Contemporary Epistemology (Second Edition). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-631-13622-3
- DeRose, Keith. 1992. "Contextualism and Knowledge Attributions", Philosophy and Phenomenological Research, 15: 213–19.
- DeRose, Keith. 1999. "Contextualism: An Explanation and Defense", in Greco and Sosa 1999.
- Descartes, Rene. 1641. Meditations on First Philosophy
- Feldman, Richard. 1999. "Contextualism and Skepticism", in Tomberlin 1999, pp. 91–114.
- Gettier, Edmund. 1963. "Is Justified True Belief Knowledge?", Analysis, Vol. 23, pp. 121–23. Online text.
- Greco, J. & Sosa, E. 1999. Blackwell Guide to Epistemology, Blackwell Publishing.
- Harris, Errol E. 1970. Hypothesis And Perception, George Allen and Unwin, London, Reprinted 2002 Routledge, London.
- Harwood, Sterling. 1989. "Taking Skepticism Seriously – And In Context", Philosophical Investigations, Vol. 12.
- Hay, Clare. 2008. The Theory of Knowledge: A Coursebook, The Lutterworth Press, Cambridge.
- Hawthorne, John. 2005. "The Case for Closure", Contemporary Debates in Epistemology, Peter Sosa and Matthias Steup (ed.): 26–43.
- Hendricks, Vincent F. 2006. Mainstream and Formal Epistemology, New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Kant, Immanuel. 1781. Critique of Pure Reason.
- Keeton, Morris T. 1962. "Empiricism", in Dictionary of Philosophy, Dagobert D. Runes (ed.), Littlefield, Adams, and Company, Totowa, NJ, pp. 89–90.
- Kierkegaard, Søren. 1844. Philosophical Fragments.
- Kirkham, Richard. 1984. "Does the Gettier Problem Rest on a Mistake?" Mind, 93.
- Klein, Peter. 1981. Certainty: a Refutation of Skepticism, Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press.
- Kyburg, H.E. 1961. Probability and the Logic of Rational Belief, Middletown, CT: Wesleyan University Press.
- Korzybski, Alfred. 1994 (1933). Science and Sanity: An Introduction to Non-Aristotelian Systems and General Semantics, Fifth Edition. Ft. Worth, TX: Institute of General Semantics.
- Lewis, David. 1996. "Elusive Knowledge." Australian Journal of Philosophy, 74, 549–67.
- Morin, Edgar. 1986. La Méthode, Tome 3, La Connaissance de la connaissance (Method, 3rd volume : The knowledge of knowledge)
- Morton, Adam. 2002. A Guide Through the Theory of Knowledge (Third Edition) Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 1-4051-0012-5
- Nelson, Quee. 2007. The Slightest Philosophy, Indianapolis, IN: Dog Ear Publishing, 296 pages.
- Niiniluoto, Ilkka. 2002. Critical Scientific Realism, Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press.
- Plato. Meno.
- Popper, Karl R. 1972. Objective Knowledge: An Evolutionary Approach, Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press.
- Preyer, G./Siebelt, F./Ulfig, A. 1994. Language, Mind and Epistemology, Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
- Rand, Ayn. 1979. Introduction to Objectivist Epistemology, New York: Meridian.
- Russell, Bertrand. 1912. The Problems of Philosophy, New York: Oxford University Press.
- Russell, Bertrand. 1940. An Inquiry into Meaning and Truth, Nottingham: Spokesman Books.
- Santayana, George. 1923. Scepticism and Animal Faith, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons – London: Constable and Co.
- Spir, African. 1877. Denken und Wirklichkeit: Versuch einer Erneuerung der kritischen Philosophie (Thought and Reality: Attempt at a Renewal of Critical Philosophy) , (Second Edition) Leipzig: J. G. Findel.
- Schiffer, Stephen. 1996. "Contextualist Solutions to Skepticism", Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society, 96:317-33.
- Steup, Matthias. 2005. "Knowledge and Skepticism", Contemporary Debates in Epistemology, Peter Sosa and Matthias Steup (eds.): 1–13.
- Tomberlin, James (ed.). 1999. Philosophical Perspectives 13, Epistemology, Blackwell Publishing.
- Wittgenstein, Ludwig. 1922. Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus, C.K. Ogden (trns.), Dover. Online text.
External links and references
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy articles:
- Bayesian Epistemology by William Talbott.
- Epistemology by Matthias Steup.
- Evolutionary Epistemology by Michael Bradie & William Harms.
- Feminist Epistemology and Philosophy of Science by Elizabeth Anderson.
- Naturalized Epistemology by Richard Feldman.
- Social Epistemology by Alvin Goldman.
- Virtue Epistemology by John Greco.
Other links:
- Synthese, An International Journal for Epistemology, Methodology and Philosophy of Science
- Research articles in Epistemology – PhilPapers
- What Is Epistemology? — a brief introduction to the topic by Keith DeRose.
- Certain Doubts — a group blog run by Jonathan Kvanvig, with many leading epistemologists as contributors.
- The Epistemological Lifeboat by Birger Hjørland & Jeppe Nicolaisen (eds.)
- The Epistemology Page by Keith DeRose.
- Justified True Belief and Critical Rationalism by Mathew Toll
- Epistemology Papers a collection of Michael Huemer's.
- Epistemology Introduction, Part 1 and Part 2 by Paul Newall at the Galilean Library.
- Teaching Theory of Knowledge (1986) — Marjorie Clay (ed.), an electronic publication from The Council for Philosophical Studies.
- Epistemology: The Philosophy of Knowledge — an introduction at Groovyweb.
- Introduction to Theory of Knowledge — from PhilosophyOnline.
- The Peripatetic A practical introduction to the theory of knowledge
- Theory of Knowledge — an introduction to epistemology, exploring the various theories of knowledge, justification, and belief.
- A Theory of Knowledge by Clóvis Juarez Kemmerich, on the Social Science Research Network, 2006.
- An Introduction to Epistemology by Paul Newall, aimed at beginners.
- Knowledge is the eye of all – Knowledge in the Upanishads
- On a Critical Epistemology
- Language Perception and Action: Philosophical Issues
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||